The "ERP"
IT being the back bone, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) covers the techniques and concepts employed for the integrated management of businesses as a whole, from the viewpoint of the effective use of management resources, and to improve the efficiency of an enterprise. ERP packages are unified (covering all business functions) software packages that support the above ERP concepts.
In the 90’s, ERP packages were targeted at the manufacturing industry, and consisted mainly of functions for planning and managing core businesses such as sales management, production management, accounting and financial affairs, and so on. However, in the last decade, adaptation not only to the manufacturing industry, but also to diverse types of industry has become possible. With the ever developing and innovating IT techniques, the expansion of implementation and use of ERP packages has been progressing on a global level.
ERP software is intentionally designed to model and automate many of the basic processes of a company. It established an effective link between the various functions of a company from the top level to the bottom level of the hierarchy, with the goal of integrating information across the company, for example, a communication channel is established between the finance department and the shop floor for information sharing,. This software helped in eliminating complex and expensive links between computer systems that were never meant to talk to each other. It also established a faultless and continues flow of information within the company.
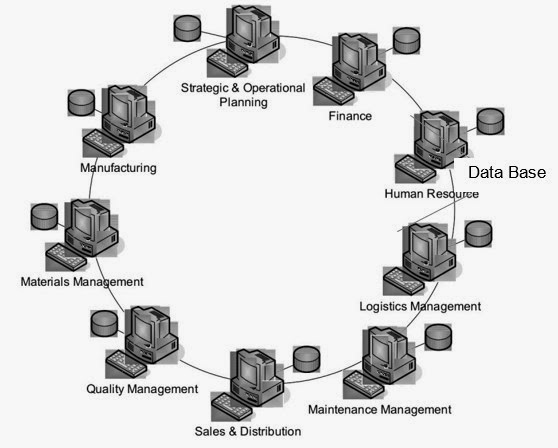 Figure 1.2 shows how information is integrated within an organisation using an ERP system. This system is similar to the Pre-ERP system but, in the ERP system all the different departments of an organisation are linked to a centralized system which stores all the information from various departments. Any department at any time can gain access to any required information from another department via ERP or from the ERP database itself. The manufacturing department can access information form quality management department via ERP system. This shows the flexibility of a system, where independent departments are bonded together as a unit and any two departments can establish communication at ease without depending on any other departments.
Figure 1.2 shows how information is integrated within an organisation using an ERP system. This system is similar to the Pre-ERP system but, in the ERP system all the different departments of an organisation are linked to a centralized system which stores all the information from various departments. Any department at any time can gain access to any required information from another department via ERP or from the ERP database itself. The manufacturing department can access information form quality management department via ERP system. This shows the flexibility of a system, where independent departments are bonded together as a unit and any two departments can establish communication at ease without depending on any other departments.
ERP software is a replica of the major business processes of an organisation, such as customer order fulfillment and manufacturing. The success of an ERP system depends on its ease for information access. A constrained ERP system is not much better than the legacy system it replaces. In lots of cases, it is worse, as the old code at least was written specifically for the company and the task.
ERP systems are a set of generic processes, they are capable of producing dramatic improvements, when used to connect parts of an organisation, and integrate its various processes seamlessly. For example, when a warehouse in Noida enters a customer order, for example, the data flows automatically to others in the company who need to see it. Data flows to the finance department at the company headquarters in Mumbai, and to the manufacturing plant in Chennai. The attractive Information Integration Techniques (IIT) of ERP was able to capture the attention of ERP vendor’s primary targets the CEOs and CFOs of various organisations, and the sales of ERP in the global market took of in early 1990’s.
